For US Healthcare Professionals
I am a
Rheumatology Specialist
For US Healthcare Professionals
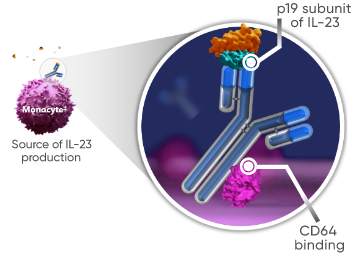
Full Prescribing InformationTREMFYA® is the only* dual-acting† IL-23i designed to neutralize inflammation at its cellular source1

‡In vitro studies were
conducted using an
inflammatory monocyte
model.
†TREMFYA® works by:
- Blocking IL-23, a cytokine responsible for inflammation
- Binding to CD64, a receptor on cells that produce IL-23
Findings for dual-acting are limited to in vitro studies that demonstrated
guselkumab’s binding to CD64 in an inflammatory monocyte model.
The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
Findings for dual-acting are limited to in vitro studies that demonstrated
guselkumab’s binding to CD64 in an inflammatory monocyte model.
CD64=cluster of differentiation 64; IL=interleukin; IL-23i=interleukin-23 inhibitor.
*”Only” based on approved IL-23 inhibitors for active PsA as of February 2025.
Reference: 1. Krueger J, Eyerich K, Greving C, et al. Differentiation of therapeutic antibodies targeting IL-23. Poster presented at: 2022 Society for Investigative Dermatology; May 18-21, 2022; Portland, OR.
TREMFYA® blocks IL-23 and regulates key pro-inflammatory cytokines1
- TREMFYA® is the only fully human IL-23i1
- TREMFYA® has been shown to decrease the elevated baseline serum levels of IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 in patients without fully blocking IL-17A/F1,2*
The clinical significance of these findings is not known.
CD64=cluster of differentiation 64; IL=interleukin; IL-23i=interleukin-23 inhibitor; MOA=mechanism of action.
*In evaluated subjects with PsA, serum levels of acute phase proteins C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A and IL-6, and Th17 effector cytokines IL-17A, IL-17F, and IL-22 were evaluated at baseline. Serum levels of these proteins measured at Week 4 and Week 24 were decreased
compared to baseline following guselkumab treatment. The relationship between these pharmacodynamic markers and the mechanism(s) by which guselkumab exerts its clinical effects is unknown.
References: 1. TREMFYA® (guselkumab) [Prescribing
Information]. Horsham, PA: Janssen Biotech, Inc. 2. Seibert S, Coates LC, Schett G, et al. Modulation of interleukin-23 signaling with guselkumab in biologic-naive patients versus tumor necrosis factor inhibitor-inadequate responders with active psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024;76(6):894-904.